What is Domain Name Server and How Does it Work
Domain Name System or DNS is the reason behind the functioning of the Internet. DNS tends to convert the web addresses entered in the web browser such as www.mywebsitename.com into 192.168.3.0. in other words, DNS helps connect the Internet on your computer, laptop, smartphone or tablet.
It does it by matching names of the website to the numbers related to the address of that particular website. Websites have an IP address in numbers such as 63.101.179.180. However, it is not easy for general users to remember these numbers and associate them with a particular website. Thus, DNS helps sync the domain names given such as Google, Yahoo, Amazon, etc. to their respective IP addresses.
Thus, all users can easily surf the Internet by entering the simple domain name instead of the complicated IP address number.
Why is DNS Necessary?
Without the phone directory, you will never be guess the phone number of any contact that you can’t memorize. In the same way, without the DNS you cannot reach a particular website on the Internet. When you type the domain name, the computer will use the DNS server to reach the website IP address. If there was no DNS, then the user would be able to reach a particular website only by typing the IP address such as 101.14.234.118 directly.
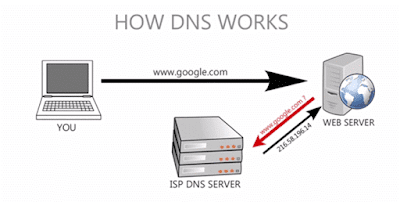
How Does DNS Work?
There is a series of steps followed by the computer to reach a particular website requested. These steps occur every time a person enters a domain name in the web browser, tries listening to music on YouTube, or sends an email.
#1 Information Request
The process of retrieving a website begins the moment the computer is asked to resolve a hostname. For example, www.mywebsite.come. The computer will first search the local DNS cache and if it does not find an answer here, it will lead to a DNS query.
#2 DNS Query
The computer will now ask for information by contacting you ISP’s recursive DNS servers. These specialized servers carry out all the basic processes for DNS query. These recursive servers have their set of caches and thus, the process usually ends at the ISP’s end and the answer is sent to the users’ computer.
#3 Reach Root Nameservers
In case the recursive server does not have an answer to the query, it will forward the request to root nameservers. This is a computer that will answer all the questions related to the domain names. It is a type of telephone switch for the DNS servers. If they can’t get an answer, they will forward the request to nameservers who can answer the query.
#4 Query Reaches the TLD Nameservers
After reading the query from right to left, that is www.mywebsite.com, the root nameserver will direct it to the Top-Level Domain (TDL) nameservers to seek .com. The TDL nameservers such as .com, .org, .us, etc. have their own nameservers. These servers contain all the information needed to reach the query like a telephone receptionist. In case they don’t find any information, the will direct the query to a server that does have the information.
#5 Request Authoritative DNS servers
The TLD nameservers will request the query directly to the specific domain. These are called as authoritative nameservers and contain all the information related to a specific domain. The information is stored in DNS records. There are different types of records with different information.
#6 Get the Query Answered
The recursive server will get information related to mywebsite.com from the authoritative nameservers. This information is then stored on their local cache. Thus, the next time you or anyone else asks for the same website, the recursive servers will have the answer ready. However, all records have a time-to-live value. This means all records have an expiration date and once the record ends, the recursive server will have to ask for information again.
#7 Send the Answer Back
The recursive server will return the A record to the computer and it will be stored on the computers cache. It will read the IP address from the record and pass the information to the browser. Thus, the website will open on your computer after getting a connection to the webserver and receive it from the website.
This entire process of domain name server takes just few milliseconds. Before you blink your eye twice, the result is flashed on your computer, tablet, or mobile screen. This is all about what domain name server is and how it works. It is very simple process with complicates steps that are vital for the functioning of the Internet.